A Revit Family is a group of objects that are combined to create a single, reusable component. Families can be created in Revit and saved for later use in other projects, making it easier and faster to add standard elements to a design.
One of the key features of Revit is the use of families, which are pre-built 3D models of common building elements such as doors, windows, furniture, columns, beams, ductwork and pipework, just to name a few types.
There are three main types of Revit Families:
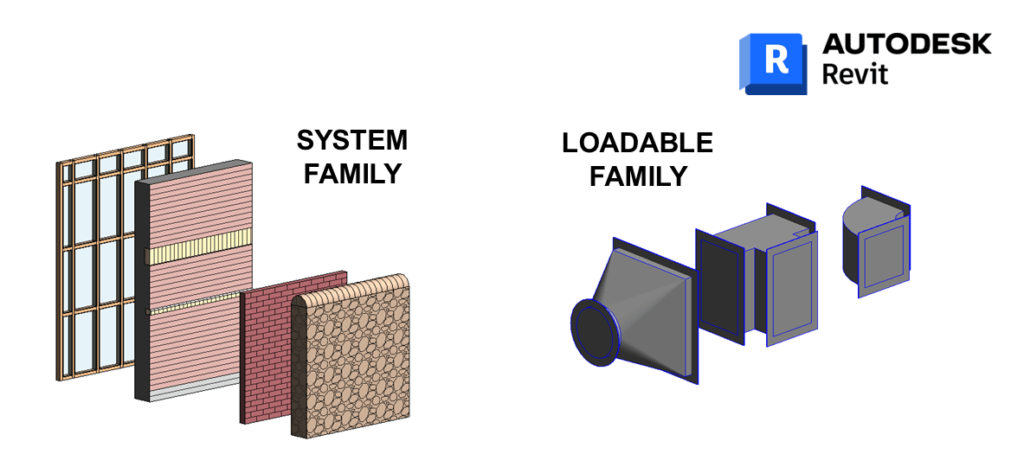
- System Families: System families are built-in elements that are used to define the basic structure of a building model. Examples of system families include walls, floors, roofs and structural columns. These families cannot be modified or deleted and are used to establish the basic framework of a building model.
- Loadable Families: Loadable families are user-created components that can be loaded into a project and placed as needed. Examples of loadable families include doors, windows, furniture and lighting fixtures. Loadable families can be customized to meet specific project requirements, and they can be saved for use in future projects.
- Model In-Place: In-place families allow users to create complex or custom components within a project, rather than using a pre-built family. These families are created and placed directly within a project. Unlike other families, in-place families cannot be saved for reuse in other projects, but you can copy from project to project.
In Revit families are classified under categories, families and family types. Below is an example of structural framing (beams). There are different families such as Universal Beams, Universal Columns, Parallel Flange Channels and so on. Then the individual sizes (UB127x76x13, UB152x89x16, UB178x102x19, UB203x102x23, UB203x133x25).

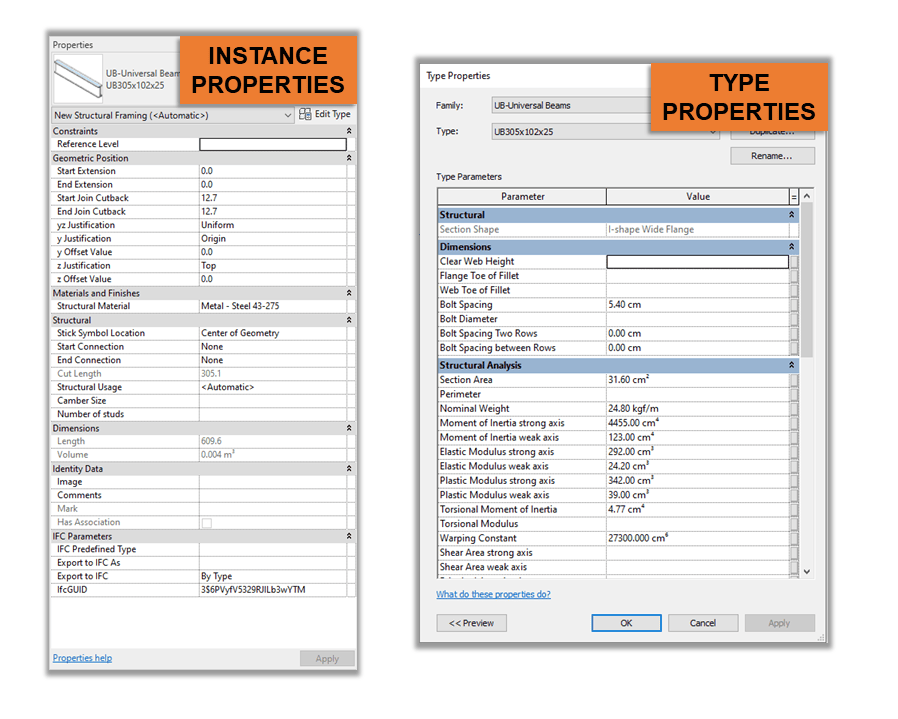
Each family has type properties, which control the information about that family type. This could be the level or work plane it is placed on or even the phase it is created on. If edited it will update across all the families of that type across the entire project. Then we have a family instance type, which is specific to that individual family and could include things like installation or warranty date, or model number.
The table below shows the different Revit family types.
| File Type | Descriptions |
| .RVT | Standard project file in Revit, where system families are stored. |
| .RFA | The file format of a component Family. Can be opened directly, inserted, or loaded into an .RVT file. (Similar to blocks in AutoCAD) |
| .RTE | The project template file. When you start a new model an .RTE file is used to create the model. When is saved as a new .RVT model. The file contains all of your company’s standards and settings. Views, sheets, and families should be set up and ready to use in the project template. (Similar to .DWT AutoCAD) |
| .RFT | The family template file. When a new family is started, an .RTE. |
There are two ways that families can be placed within your Revit project.
- Host-Based Families: Hosted families are those that are dependent on an host. Such hosts are walls, ceilings, floors, roofs or a face.
- Stand-Alone Families: Stand-alone families are those that don’t need a host, for example, a desk or a chair.
Websites to download customer Revit family libraries
- BIM Store (UK): BIMStore.co
- NBS National BIM Library (UK): nationalbimlibrary.com/en-gb/
- BIM Object: bimobject.com
Also, check with your local manufacturer as many now provide Revit families for us to use in our projects.
Revit Family Training and Support
If you need any help understanding Revit or need help getting started or struggling to build your own Revit families. Then why not get in touch with us here at Man and Machine? We have a number of courses we run to help users. Check out the link: Man and Machine Revit Courses.
For more information on this blog post or if you have any other questions/requirements, please complete the below form: